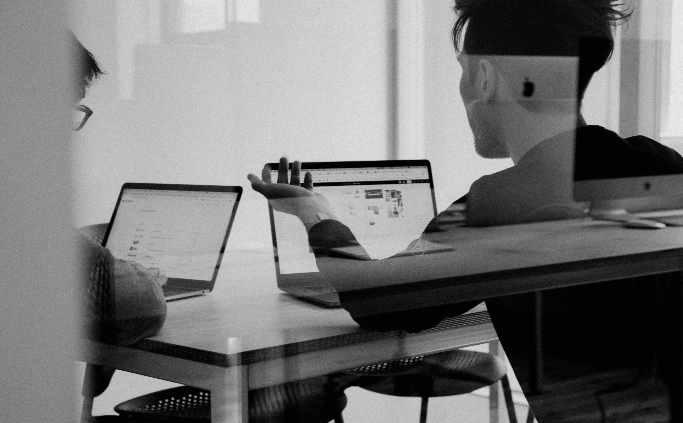
Banking & Financial Services
Agile Transformation in a major Saudi Bank
Our approach to agile transformation for a traditional banking organisation.
Background
A major Saudi Bank approached iNQ to support in an agile transformation, beginning with classroom training and evolving into ‘on the job’ consultation and and knowledge transfer into the technical teams.
Our aim was to create a scalable structured framework for teams to follow so they can execute projects using Agile Scrum confidently after we have left. Arming the teams with the knowledge and practice to become ‘Agile ambassadors’ to scale and champion Agile inside the business.
OUR
APPROACH
We Assess the Agile maturity of the organisation with our iGNITE ™ process to establish how far the organisation is along the Agile journey as well as providing us with insights into the business context and its main challenges.
We planned a two phase approach, which started with classroom training to align the Agile understanding across the business and to provide the foundations for a full Agile transformation.
The Agile Transformation focussed on our 4 key pillars of change; people, process, technology and structure. A scalable framework was developed so teams were able to confidently execute Agile projects long after we had gone.
We appointed Agile ambassadors across each department who became accountable for upholding Agile practice in the organisation.
Solution
We conducted an agile maturity assessment using iGNITE ™, the organisation was low on the agile maturity matrix so we approached the transformation in three phases.
Classroom Training
Classroom training was conducted to ensure there is an aligned understanding across the organisation.
Agile Pilot
Implemented the agile framework into a small ‘test team’ who delivered pilot projects using agile scrum.
Agile Transformation
Scaled the agile pilot focussing on leadership buy in, team structure, process, technology and tools.
THE 4 PILLARS OF CHANGE
1
Structure
We restructured teams to be extremely efficient at executing Agile scrum
2
Process
We created a scrum framework, focussing on sprint process, ceremonies, tools and artifacts.
3
Technology
We ensured the organization had the appropriate infrastructure and operations to support rapid change.
4
Tools
We introduced collaborative tools for communication and sprint management such as, Jira, Slack and Miro.
Results
Faster ROI
Reduce Risks
More opportunity to inspect and adapt through the process, allows for the team to exercise higher rigor and control.
Allows for change
Higher Quality Product
Rapid iteration in development means short functional cycles which allows for early feedback and better end product.
Increased Ownership
Agile teams are self organising, they work collaboratively to get work done
User Focus
The user is at the heart of every decision to ensure that the end product is usable, valuable and meaningful.
Faster ROI
Reduce Risks
More opportunity to inspect and adapt through the process, allows for the team to exercise higher rigor and control.
Allows for change
Higher Quality Product
Rapid iteration in development means short functional cycles which allows for early feedback and better end product.
Increased Ownership
Agile teams are self organising, they work collaboratively to get work done
User Focus
The user is at the heart of every decision to ensure that the end product is usable, valuable and meaningful.
CONCLUSION
Traditional banking organisations are relatively late adopters to agile practices due to tight legislation and legacy systems. However, in order to stay competitive in such a fast paced and data driven climate, the banking industry must be able to adapt to change quickly and keep the customer at the heart of the decision making process. This can only be done by embracing agile methods and becoming agile powerhouses.

